Network Configuration
Network Protocol
Neither Master Patch or Stage Viewer use a bespoke networking protocol for communication, this means that neither application need any specific networking settings configured in order to operate, and can happily coexist on existing networking infrastructure.
This means that both applications can easily run along side Dante, MILAN, Ravenna, or any other audio networking protocol without the need for quality of service (QoS) or other higher level network programming.
Both Master Patch and Stage Viewer use simple TCP-IP communication methods, connections to viewer applications are established with a TCP connection.
Physical deployment
There are numerous ways to set up a network, a full network deployment instruction is out of the scope of this document, however, below are detailed some examples of how a user can set up their physical network when deploying a Master Patch and Stage Viewer system.
Wireless
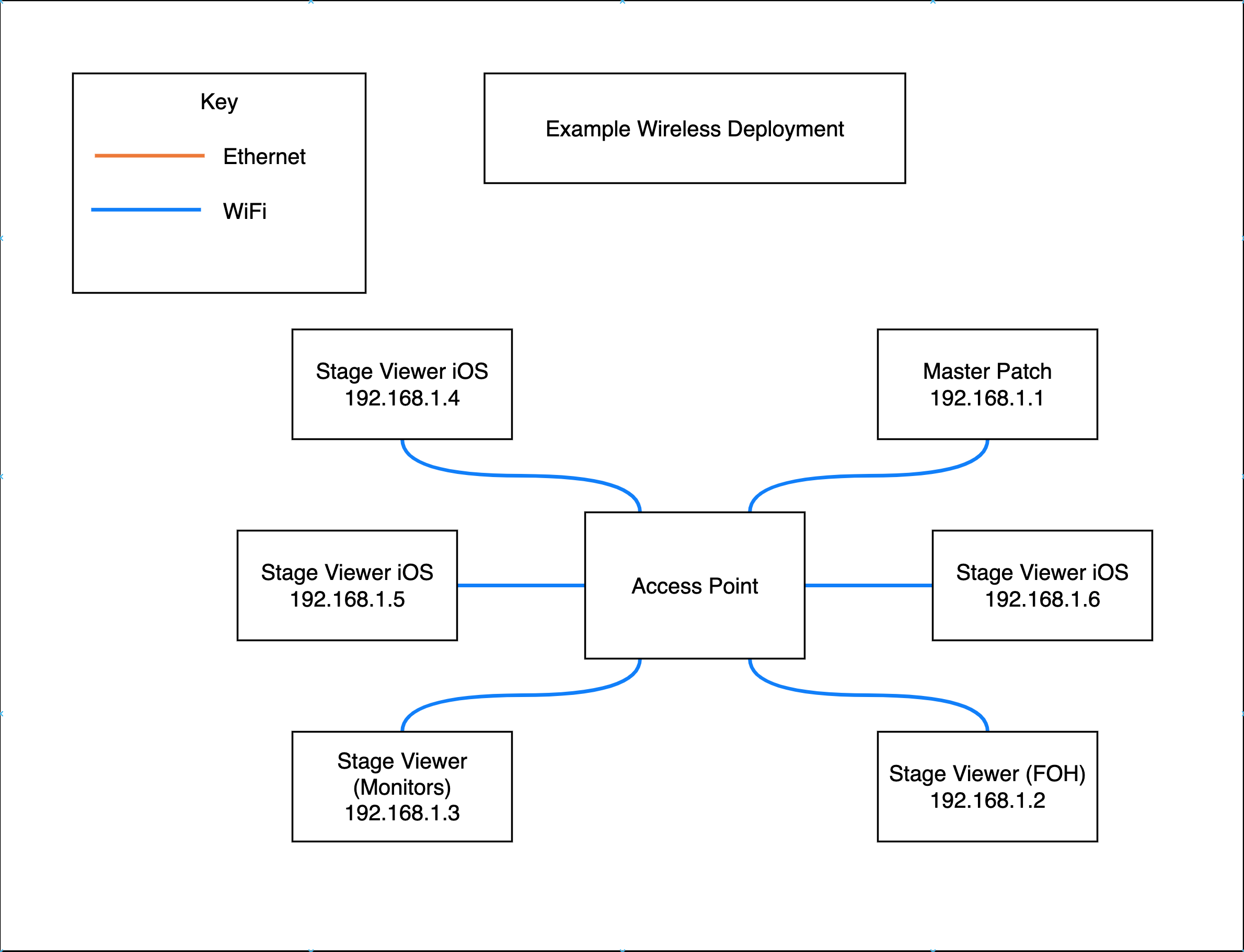
One way to deploy a system is completely wirelessly using a Wi-Fi network, the strengths and weaknesses of this type of system deployment are detailed below.
| Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|
| Allows a high level of user mobility as they are not physically connected | Large files can take longer to transfer between a server and a client |
| Effective for small coverage areas | Potentially congested Wi-Fi production environment could cause slow connections or loss of connections as distance from access points increases |
| Allows user to be physically distanced from networking hardware, allowing flexibility in workstation placement | |
| Less dedicated hardware needed |
Example Wireless deployment
Wired
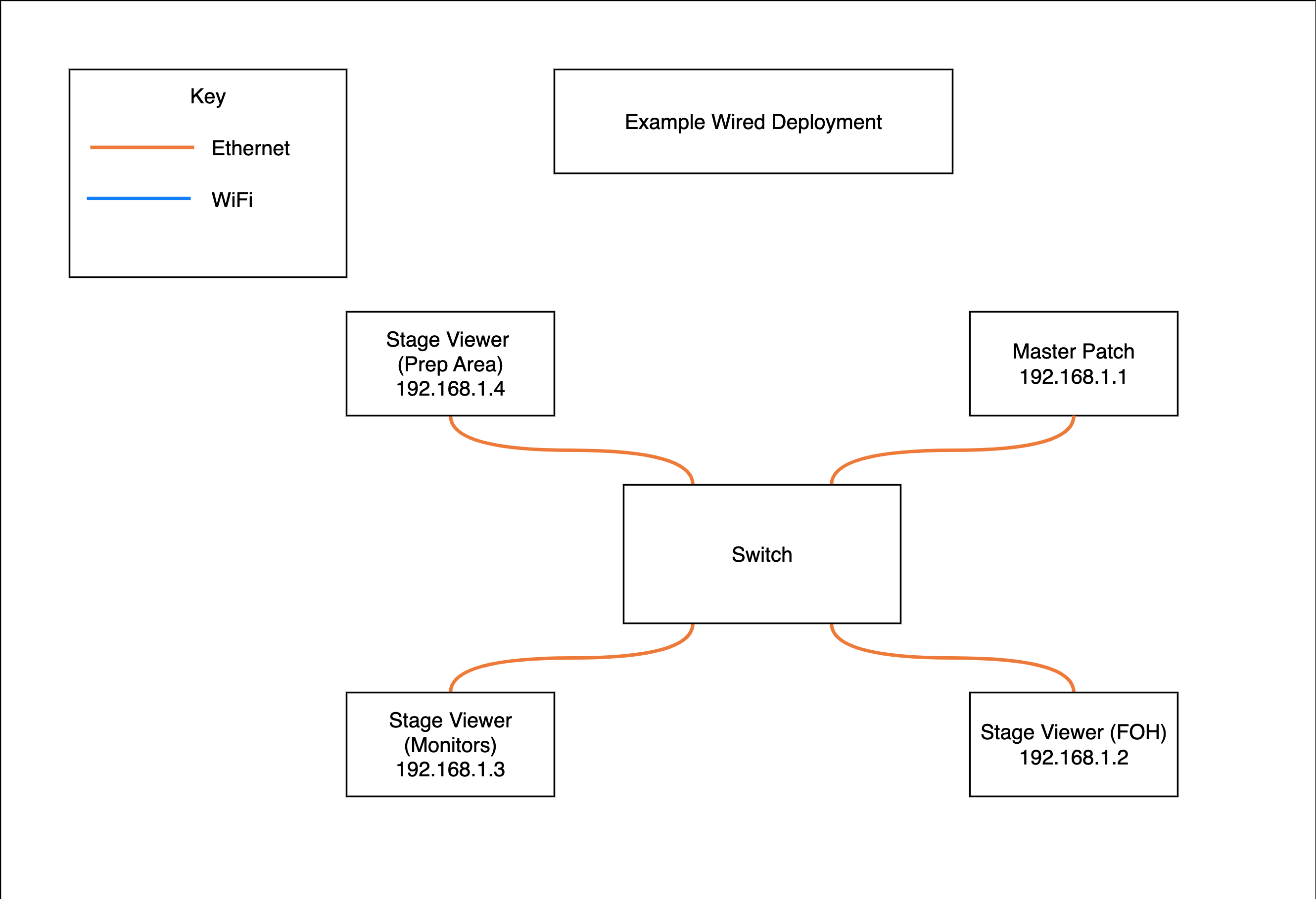
Another way to deploy a system is entirely wired, not using any wireless solutions, the strengths and weaknesses of this type of system deployment are detailed below.
| Strength | Weakness |
|---|---|
| Very high data transmission rate; without a wireless bump in the network all users have the quickest possible connection to the server | Decreased user mobility; a user is physically connected to the network meaning they are not able to move and still use the system |
| Allows for extension of the coverage of the system, using Fibre or Copper cable users can be potentially kilometres from the server | More dedicated hardware needed such as switches and physical cabling which comes with increased chance of errors and hardware failures |
Example Wired deployment
Hybrid
For most use cases, a combination of both wired and wireless deployments is the best answer. Users can take the benefits of both systems to achieve an effective deployment.
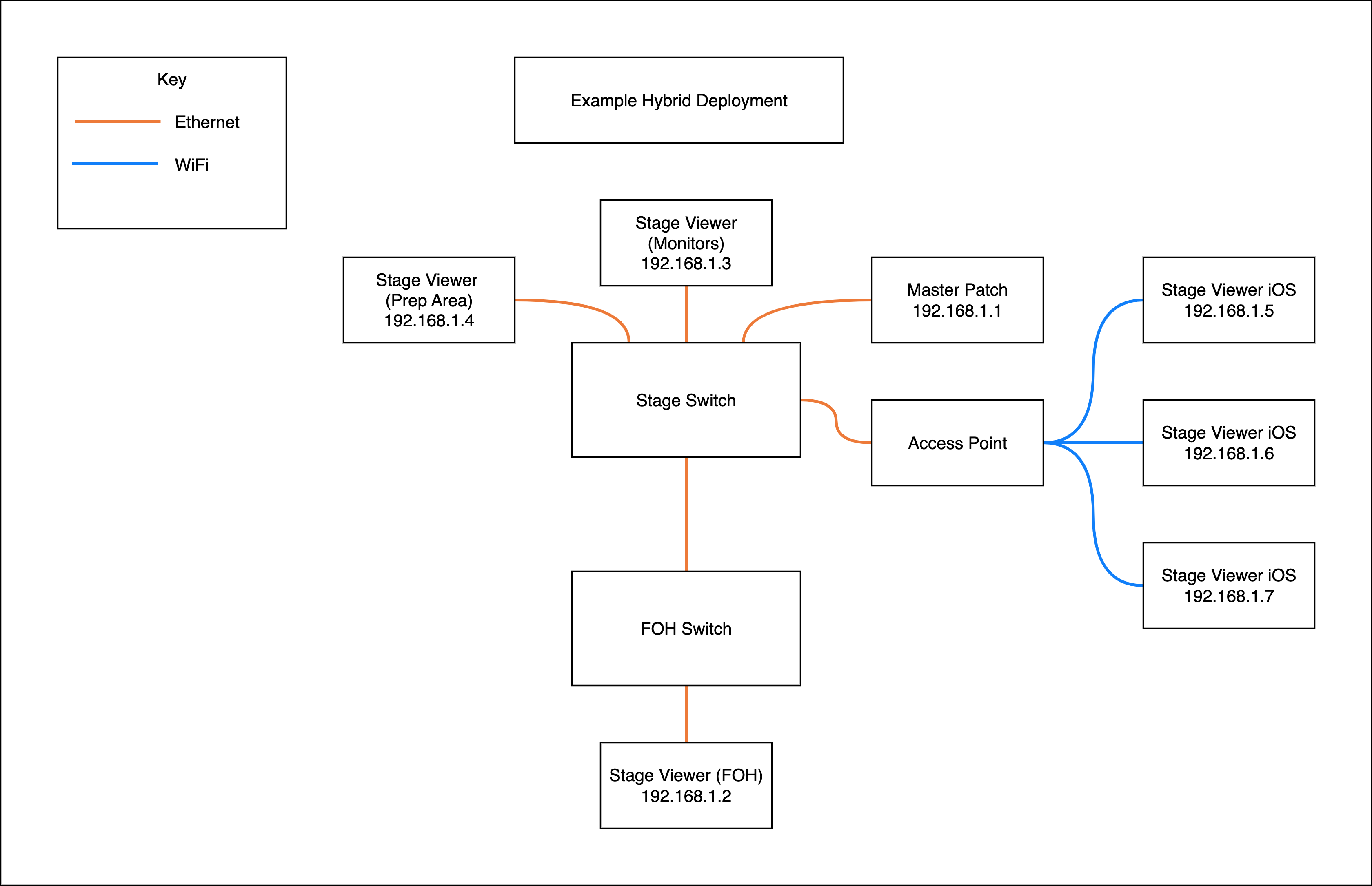
For example, if a production has a monitor mix position and a front of house mix position, it would make sense to hard-wire the Master Patch machine and the monitor mix Stage Viewer machine to the same switch, run a cable to the front of house mix position, connect to a switch there, and then hard-wire into the front of house switch with the front of house Stage Viewer machine, then on stage an Access point can be deployed allowing stage technicians to use portable devices to access Master Patch.
Using this deployment, critical positions with little mobility such as the mix engineers are hardwired ensuring the most secure and performant connection to the server, while stage team members who need to be mobile in order to serve the stage can access data wirelessly thanks to the Access Point.
Example Hybrid deployment
Common Troubleshooting
Even with the best laid plans, things can still sometimes go wrong, detailed below are some common solutions to problems people can have when first setting up a network.
IP Address conflicts
Make sure that none of the devices on the network share the same IP Address. IP Addresses should be unique per device on the network.
Firewalls
If experiencing issues with connection, check the firewall settings of the devices on the network to ensure the device firewall is not blocking network traffic from Master Patch or Stage Viewer.
A good method to check if connection is achievable is to 'ping' devices using the operating system command line application, if a ping fails, then there is a good chance there is a firewall on one of the machines blocking network traffic or that the connection (wired or wireless) between the machines is not correctly established.
When first opening Master Patch or Stage Viewer on a Windows Machine, the operating system will ask the user if they want to allow the application to use local public and private networks to access the application, the user should Allow these connections.
Faulty cabling
Ensure that all cabling is in good condition, check pins to make sure all pins are terminated correctly and in good working order, ensure the cable is not of a 'crossover' type.
Managed networks
If using a managed network, ensure that all devices on the network are connected to the same VLAN, and that the network is not blocking traffic on any of the ports which a device is connected to.